A. Technical Specifications
1. Military Specifications
All color variations of CARC must meet stringent military specifications. The typical formulation of these finishes consists of three primary groups of raw materials: the resin or binder system, the pigment package, and the solvents.
As a means of standardizing the paint formulations manufactured by private contractors for the military, the system of military specifications (MIL SPEC) is used. The military specification lists all the requirements of the paint, which describes types and composition of materials, color and spectral reflectance properties, and label markings.
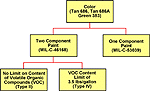
One of these military specifications, MIL-C-46168 specifies a two-component system and references nineteen colors, including Tan 686A. The specification is available in two types, type II and type IV. Type II is the older version with a standard amount of volatile organic compounds (VOC). Type IV is a modified formula that has a reduced VOC content of up to 3.5 pounds per gallon or 420 grams per liter..[176] Volatile organic compounds can be an occupational health hazard, as well as an environmental concern. VOCs react with the atmosphere, resulting in the production of air pollutants that are components of smog. Volatile organic compounds are also a source of occupational health hazards.
The other topcoat specification is MIL-C-53039, a single component system. MIL-C-53039 references nineteen colors with Tan 686A as one its colors. This specification has only one type and has a VOC content that does not exceed 3.5 pounds per gallon or 420 grams per liter.[177] Both the two-component and one-component paint systems were used in theater.[178] See Tab D for a chart showing the different colors and variations of CARC used in theater.
2. Qualified Products List
The military uses the qualified products list as another control measure to ensure the consistency, quality, and performance of its paints. The qualified products list (QPL) is a list of approved suppliers. The Army Research Laboratory has rigorously tested the products of the manufacturers listed on the QPL for conformance to all specifications of performance and composition. Only products from suppliers listed on the QPL are normally procured for use on government material.[179]
B. CARC Paint Formulations
The resin systems used in the Army’s camouflage coatings are polyureas and polyurethane-type materials. The pigments can be a variety of colors and provide the low-gloss properties as well as color to the paint. The solvents used are generally standard hydrocarbon-based materials that assist in package viscosity and spraying properties. The following formulations are representative of two component, or MIL-C-46168, camouflage coatings, and list the major ingredients found in these paints. Note that the formulations for the tan and green coatings are very similar, with the principle differences residing in the pigments. (Note: Information provided by US Army Research Laboratory.)
As discussed in this report, Tan 686 was used initially in the Kuwait theater of operations. A modified version of this paint, Tan 686A, was later used due to its ability to reduce the amount of solar heat vehicles would absorb. Green 383 was used during the redeployment painting operation. Figure 11 shows the different variations of the CARCs used in theater. Note that there is a two component and one component version of each paint, both of which were used in theater. Also, there were two different types of the two component paint used, Type II and Type IV.
Figure 11. CARC variations used in-theater
Resin: Hexamethylene diisocyanate (HDI), Bayer Desmodur N751
Solvent: N-Butyl acetate - viscosity and spray properties
| First Page | Prev Page | Next Page |